Key Concepts
Read through the following concepts for a better understanding of some of the key concepts in SiteContinuity. It will help you navigate the planning and preparation for the DR operations in your DR plan.
Sites
To facilitate DR operations in SiteContinuity, you need to designate Cohesity clusters as sites and map them to specific locations. As SiteContinuity is an as-a-Service solution offered via Helios, connect the clusters to Helios before designating the clusters as sites.
If the primary IT infrastructure becomes unavailable, the applications are replicated from the primary site to a secondary or DR site to resume operations with minimal disruption. For this reason, designate separate Cohesity clusters for the primary sites and DR sites. Map clusters that protect your applications as Primary sites. Map clusters to which you want to replicate the applications as DR sites.
For details on how to map a Cohesity cluster to a site, see Add Sites.
DR Plan
To facilitate DR orchestration, you must create a DR plan. A DR plan is a business plan that defines which DR Applications can be effectively brought up and where (DR site). SiteContinuity offers a simple, easy-to-use interface to create DR plans that consists of DR Applications, primary and DR sites, and Resource Profiles. For details on how to create a DR plan, see Create a DR Plan.
DR Application
A DR Application allows you to specify the orchestration order of VMs with the ability to insert executable scripts and time delays. Orchestration order is the sequence by which the VMs are brought online and to an operational state on a site. You can group the VMs in the DR application into multiple VM Groups.
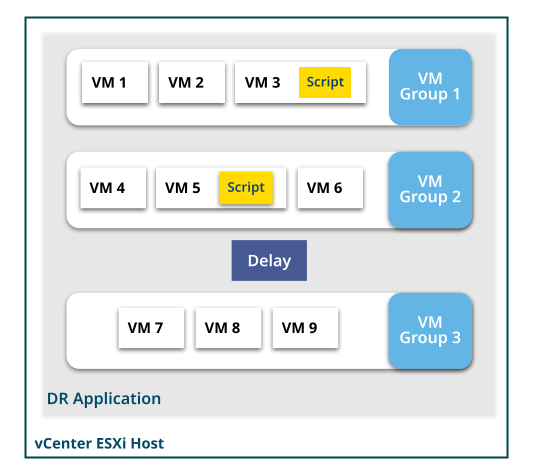
SiteContinuity executes the components of the DR Application in the order in which they are defined in the DR plan. The VMs within a VM Group (along with scripts applied on the VMs) are executed concurrently. For example, in the above image, VM Group 1 is executed first, followed by VM Group 2. After the delay, VM Group 3 is executed. When VM Group 1 is executed, VM 1, VM 2, and VM 3, along with its script, are executed concurrently.
A DR Application is mapped with a single vCenter registered on the primary site. For details on how to create a DR Application, see Create DR Application.
VM Group
A VM Group is a logical grouping of VMs that represents a specific tier in your application. For example, if you have a multi-tier application that consists of several VMs (some running databases, some applications, and others web services), you can create a VM Group for each tier (such as Database tier, Application tier, and Web tier).
Custom Scripts
Custom scripts are user-defined scripts that can run on VMs. Use these scripts to run configuration changes on the failed over or failed back VMs. For security purposes, SiteContinuity requires that you provide the credentials of the VMs to apply a custom script. An uploaded script is saved only after the authentication of the provided credentials are verified. For VMs running on Windows OS, Cohesity supports batch scripts, and for VMs running on Linux OS, Cohesity supports bash scripts.
Time Delay
You can add time delays to your DR plan. SiteContinuity pauses the DR execution for the defined interval before resuming the operation. For example, if the delay is defined as 10 seconds in the above image, SiteContinuity would wait for 10 seconds after executing VM Group 2. After the delay, VM Group 3 is executed.
Resource Profile
Resource Profile is a combination of a Default Resource Set and one or more Custom Resource Set. A DR plan can have multiple Resource Profiles.
The Resource Profile needs to be redefined every time you perform a Test or Actual Failover or Failback because the vCenter settings specific to each VM used in the previous operation are no longer applicable when working with a new set of VMs in the sites.
Default Resource Set
When creating a Disaster Recovery (DR) plan, you define a Default Resource Set, which consists of a collection of Data Center settings. SiteContinuity applies these Data Center settings to all VMs defined in the DR plan after a Failover event. Similarly, you need to define a Default Resource Set when failing back VMs to the primary site. The Data Center settings in the Default Resource Set are:
-
Data Center. An aggregation of selected objects in the vCenter inventory that is needed for the virtual infrastructure, such as the VMs, clusters, networks, and data stores, to work. An organization can have multiple Data Centers.
-
Cluster. A collection of ESX/ESXi hosts and associated VMs intended to work together as a unit.
-
Resource Pool. A resource pool is the collection of VMs. Resource pools can be grouped into hierarchies for partitioning available CPU and memory.
-
Data Store. A virtual storage entity created by VMware ESX/ESXi hosts as a repository for the log files, scripts, configuration files, and virtual disks of the VMs.
-
Network. In a Data Center, the network enables the communication between VMs, virtual servers, and data center locations.
-
DNS Server. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or Static Domain Name System (DNS) servers to translate domain names into IP addresses.
Custom Resource Set
Custom Resource Sets override the Default Resource Set for specific VMs. By creating Custom Resource Sets, you can apply unique settings to one or more VMs. You can create as many Custom Resource Sets as needed.
RPO
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) indicates the data loss a business can tolerate. When disaster strikes, RPO defines how far you can roll back to the last usable snapshot. With SiteContinuity, you can achieve a Recovery Point Objective (RPO) of 15 minutes. This means that in the event of a disaster, you can recover your applications to a state as near as 15 minutes before the occurrence of the disaster, resulting in reduced downtime and data loss.
RTO
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) refers to the downtime a business can tolerate in a disaster.
Continuous Data Protection
Cohesity’s CDP provides 15-min RPOs for applications in VMware environments. If you want to recover your VMware VMs from any point in time, then you must enable CDP. For more information, see Cohesity CDP for VMware.
